The burgeoning field of wearable health technology offers unprecedented opportunities to improve Wearable Health Tech the lives of senior citizens. These innovative devices, ranging from simple fitness trackers to sophisticated medical alert systems, are transforming how we monitor, manage, and improve the health and well-being of older adults. This exploration delves into the market landscape, benefits, challenges, and future innovations shaping this rapidly evolving sector, providing a comprehensive understanding of its impact on senior care and independent living.
From tracking vital signs and promoting physical activity to facilitating medication adherence and providing timely emergency assistance, wearable technology empowers seniors to maintain their independence and actively participate in their healthcare. This review examines the various devices available, their effectiveness in managing chronic conditions, and the potential to mitigate the challenges associated with aging. We also consider the ethical implications and future trends that will further shape the role of wearable technology in senior healthcare.
Market Overview of Wearable Health Tech for Seniors

The market for wearable health technology specifically designed for seniors is experiencing significant growth, driven by an aging global population and increasing awareness of the benefits of remote health monitoring and preventative care. This sector offers a compelling opportunity for technology companies and healthcare providers alike, presenting innovative solutions to address the unique health needs and challenges faced by older adults.The market is characterized by a diverse range of devices and services, each catering to specific needs and preferences.
This creates a dynamic landscape with continuous innovation and competition. Accurate market sizing is challenging due to the rapidly evolving nature of the technology and varying definitions of “wearable health tech,” but reliable sources indicate substantial and consistent growth.
Market Size and Growth Projections
The global market for wearable health tech for seniors is substantial and projected to expand considerably in the coming years. While precise figures vary depending on the source and definition used, reports consistently point to a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) in the double digits. For example, a report by [Insert credible market research firm and report name here] estimated the market size at [Insert estimated market size and year] and projected it to reach [Insert projected market size and year].
This growth is fueled by factors such as increasing geriatric populations in developed and developing countries, rising healthcare costs, and a growing preference for convenient, at-home health monitoring solutions. This trend is further supported by government initiatives promoting telehealth and remote patient monitoring in many countries.
Key Players and Market Share
Several key players dominate the wearable health tech market for seniors, each with its unique strengths and market focus. These include established technology companies like Apple (with its Apple Watch), Samsung (with its Galaxy Watch series), and Fitbit (with its range of fitness trackers). Specialized companies focused solely on senior health solutions also hold significant market share, offering devices with features tailored to the specific needs of older adults.
Determining precise market share is difficult due to the lack of publicly available, granular data from all players, but these companies are consistently ranked among the leaders. Further, many smaller companies and startups are entering the market with innovative solutions, increasing competition and driving innovation.
Types of Wearable Health Tech Devices for Seniors
The market offers a diverse range of wearable health tech devices tailored to the needs of seniors. These include:
- Smartwatches: These devices offer a combination of fitness tracking, health monitoring, and communication features, often including fall detection and emergency SOS capabilities.
- Fitness Trackers: These devices primarily focus on tracking physical activity, sleep patterns, and heart rate, providing valuable data for monitoring overall health and well-being.
- Medical Alert Systems: These devices, often integrated into wearables, provide immediate access to emergency services in case of falls or other medical emergencies.
- Medication Reminder Devices: These wearables remind users to take their medications on time, helping to improve medication adherence and prevent potential health complications.
- Smart Hearing Aids: Integrating technology into hearing aids offers features like connectivity to smartphones and remote hearing adjustments.
Comparison of Wearable Health Tech Devices
The following table compares four different wearable health tech devices for seniors, highlighting their features, price points, and target users. Note that pricing can vary depending on retailer and specific features.
| Device | Key Features | Price Point (USD) | Target User |
|---|---|---|---|
| Apple Watch Series 8 | ECG, fall detection, blood oxygen monitoring, GPS, cellular connectivity, app ecosystem | $400+ | Tech-savvy seniors with active lifestyles |
| Fitbit Charge 5 | Heart rate tracking, sleep tracking, stress management tools, SpO2 sensor | $150+ | Seniors seeking basic fitness and health tracking |
| Medical Alert System with GPS (e.g., Life Alert) | Emergency button, GPS location tracking, two-way communication with emergency services | $30+/month | Seniors with mobility limitations or increased fall risk |
| [Insert another relevant device and its manufacturer here] | [List key features] | [Price range] | [Target user profile] |
Benefits and Features of Wearable Health Tech for Seniors
Wearable health technology offers significant advantages for improving the health and well-being of seniors, promoting independent living, and reducing the burden on caregivers. These devices provide a convenient and accessible way to monitor vital signs, track activity levels, and manage chronic conditions, ultimately leading to a better quality of life for older adults. The benefits extend beyond simple health monitoring; they contribute to a sense of security and empowerment, allowing seniors to remain active and engaged in their daily lives.Wearable health technology provides several key benefits for seniors, impacting various aspects of their health and daily routines.
The data collected by these devices empowers both seniors and their healthcare providers to make informed decisions about health management and preventative care. This proactive approach can lead to earlier detection of potential problems, reducing the severity of health complications and improving overall outcomes.
Improved Chronic Condition Management
Wearable devices equipped with sensors can continuously monitor vital signs such as heart rate, blood pressure, and blood glucose levels. For individuals with heart disease, continuous heart rate monitoring can detect irregular heartbeats (arrhythmias) or other abnormalities that may require immediate medical attention. Similarly, continuous glucose monitoring systems integrated into smartwatches or patches can help individuals with diabetes manage their blood sugar levels more effectively, preventing dangerous spikes or drops.
This constant monitoring allows for timely intervention and adjustments to medication or lifestyle choices, preventing serious health events. For example, a wearable device alerting a senior to a dangerously low blood sugar level could prevent a debilitating hypoglycemic episode.
User-Friendly Design and Accessibility Features
Many wearable devices are designed with the specific needs of older adults in mind. Large, easy-to-read displays, simplified interfaces, and intuitive controls are common features. Some devices also offer voice-activated controls, eliminating the need for fine motor skills. The availability of various form factors, such as wristbands, pendants, and patches, ensures that there is a suitable option for individuals with different levels of dexterity and mobility.
For instance, a large-buttoned smartwatch with clear visual cues might be preferable for a senior with limited vision or dexterity compared to a smaller, more complex device.
Enhanced Independent Living and Reduced Caregiver Burden
Wearable health technology plays a crucial role in promoting independent living among seniors. By providing continuous monitoring and alerts, these devices can reduce the need for constant supervision and intervention. For example, a fall detection feature can automatically alert emergency contacts if a senior falls, ensuring prompt assistance. Similarly, location tracking capabilities can provide peace of mind to both the senior and their family, especially for those with cognitive impairments who may wander.
This increased independence can significantly improve the quality of life for seniors and reduce the stress and burden on caregivers. The ability to remotely monitor a loved one’s health status also allows caregivers to intervene proactively, potentially preventing serious health complications.
Challenges and Limitations of Wearable Health Tech for Seniors
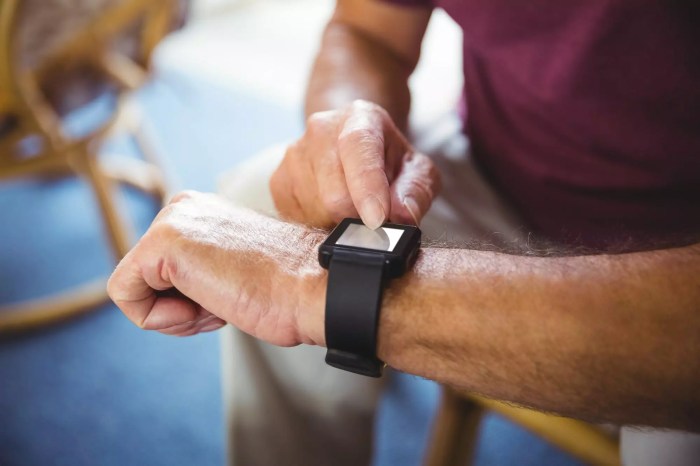

The adoption of wearable health technology by seniors presents a unique set of challenges, stemming from both the technology itself and the characteristics of the elderly population. While offering significant potential benefits, successful implementation requires careful consideration of these limitations to maximize effectiveness and ensure equitable access.
Technological Literacy and User Friendliness
Many older adults lack the technological literacy required to effectively use wearable health devices. Complex interfaces, intricate setup procedures, and the need for smartphone integration can create significant barriers to adoption. For example, the reliance on touchscreen interfaces, while intuitive for younger generations, can be difficult for seniors with dexterity issues or limited eyesight. Furthermore, the need to download and manage apps, understand data interpretations, and troubleshoot technical problems presents a steep learning curve for many.
This necessitates the development of devices with simplified interfaces, larger displays, and intuitive navigation systems. Clear, concise, and easily accessible instructional materials are also crucial.
Cost and Accessibility
The cost of wearable health technology can be prohibitive for many seniors, particularly those on fixed incomes or with limited access to healthcare subsidies. The initial purchase price, ongoing subscription fees for data analysis and support services, and the potential need for replacement devices contribute to the overall expense. Furthermore, the availability of affordable and reliable devices varies significantly across different regions and socioeconomic groups, exacerbating existing health disparities.
Initiatives to reduce the cost of devices and offer financial assistance programs are necessary to ensure equitable access.
Privacy and Data Security Concerns
Concerns regarding the privacy and security of personal health data collected by wearable devices are a significant barrier to adoption. Seniors may be hesitant to share sensitive information with technology companies or healthcare providers, particularly if they are unsure about the security measures in place. Data breaches and the potential for misuse of personal health information are major concerns.
Building trust through transparent data handling practices, robust security protocols, and clear communication about data usage policies is essential to alleviate these concerns. This includes providing seniors with control over their data and options for data anonymization or deletion.
Accuracy and Limitations of Current Technology
Current wearable health technology, while constantly improving, has limitations in accurately monitoring and assessing the health status of seniors. Factors such as variations in skin tone, body composition, and the presence of pre-existing medical conditions can affect the accuracy of measurements. For example, heart rate monitors may not be as reliable in individuals with certain heart conditions, and activity trackers may not accurately reflect the physical activity levels of individuals with mobility limitations.
Ongoing research and development are necessary to improve the accuracy and reliability of wearable sensors and algorithms, particularly for elderly populations with diverse health needs.
Effectiveness in Addressing Specific Health Needs
The effectiveness of different wearable health tech solutions in addressing the specific health needs of the elderly varies considerably. While some devices effectively monitor chronic conditions like heart disease or diabetes, others may provide limited value in addressing issues like cognitive decline or social isolation. For example, a fitness tracker might be highly effective for promoting physical activity in a relatively healthy senior, but less helpful for someone with severe mobility limitations.
A more comprehensive approach is needed, considering the diverse health challenges faced by the elderly population, and matching technology solutions to individual needs. Tailored interventions, combining wearable technology with other support services, are likely to yield the best outcomes.
Addressing the Challenge of Technological Literacy
A multi-pronged approach is necessary to overcome the challenge of technological literacy among seniors. This plan focuses on community-based education and support:
- Establish Senior-Friendly Tech Centers: Create community centers equipped with accessible technology and trained personnel to provide hands-on instruction and personalized support. These centers could offer workshops covering device setup, data interpretation, and troubleshooting.
- Partner with Local Libraries and Community Organizations: Leverage existing community resources to offer technology training sessions and provide access to devices. This broadens reach and leverages existing infrastructure.
- Develop Simplified User Interfaces and Instructional Materials: Collaborate with technology developers to create devices with intuitive interfaces, large, clear displays, and easily accessible instructions in multiple formats (printed, audio, video).
- Peer-to-Peer Support Programs: Train tech-savvy seniors to mentor their peers, providing personalized assistance and building community engagement. This fosters trust and addresses individual needs more effectively.
Future Trends and Innovations in Wearable Health Tech for Seniors
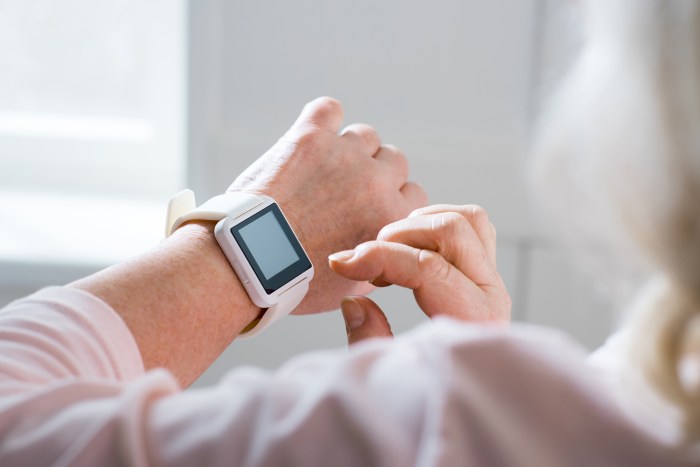

The field of wearable health technology for seniors is rapidly evolving, driven by advancements in miniaturization, sensor technology, artificial intelligence, and data analytics. These advancements promise to deliver more sophisticated, user-friendly, and effective tools for monitoring health, managing chronic conditions, and improving the overall quality of life for older adults. We can expect to see a significant increase in the adoption and integration of these technologies into both healthcare systems and the daily lives of seniors in the coming years.The integration of emerging technologies is poised to revolutionize the capabilities of wearable health devices for seniors.
This will lead to more personalized and proactive healthcare, enabling earlier detection of health issues and more effective interventions. This shift towards proactive, personalized care is particularly crucial for an aging population with increasing prevalence of chronic diseases.
Advanced Sensor Technologies and Data Analytics
Miniaturization and improved sensor technology will allow for more accurate and comprehensive health data collection. This includes advancements in bio-sensors that can monitor a wider range of physiological parameters, such as blood glucose levels, blood pressure, heart rate variability, and even subtle changes in gait or posture. Sophisticated algorithms and machine learning techniques will then analyze this data to identify patterns and predict potential health risks, allowing for timely interventions and personalized treatment plans.
For instance, a wearable device could detect a subtle change in gait that might indicate an increased risk of falls, prompting the user and their caregivers to take preventative measures.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning Integration
AI and machine learning will play a pivotal role in enhancing the intelligence and functionality of wearable health devices. AI-powered algorithms can analyze complex patterns in physiological data, identify anomalies indicative of potential health problems, and provide personalized recommendations for lifestyle changes or medical interventions. This could include predicting the likelihood of a heart attack based on heart rate variability patterns or detecting early signs of cognitive decline through analysis of sleep patterns and cognitive tests conducted through the device.
Companies like Apple are already incorporating AI-driven health features into their smartwatches, showing the growing potential of this technology.
Improved User Interfaces and Accessibility
Future wearable health devices for seniors will likely feature more intuitive and user-friendly interfaces, designed to accommodate the varying levels of technological proficiency among older adults. This includes larger, clearer displays, simplified menus, voice control features, and haptic feedback mechanisms. Design considerations will also focus on ease of use, comfort, and aesthetics, ensuring that devices are both functional and appealing to senior users.
Examples include larger buttons, simplified menu structures, and devices designed to be easily attached and removed.
Integration with Smart Home and Healthcare Systems
The integration of wearable health technology with smart home devices and electronic health records (EHRs) will create a seamless ecosystem of care. Data collected by wearable devices can be automatically shared with caregivers, physicians, and other healthcare providers, facilitating remote monitoring and timely interventions. This could involve integration with smart home systems to automatically alert emergency services in case of a fall or other health emergency, providing a crucial safety net for seniors living independently.
Several companies are already exploring such integrations, aiming to create a connected care system that supports independent living while providing timely support when needed.
Five Key Innovations Shaping the Future of Wearable Health Tech for Seniors
The following five innovations are poised to significantly impact the field:
- Predictive Analytics for Early Disease Detection: Wearables utilizing AI to analyze physiological data and predict the onset of chronic diseases like heart failure or dementia, allowing for early intervention and preventative care.
- Advanced Bio-Sensor Technology: Miniaturized and non-invasive sensors capable of continuously monitoring a wider range of vital signs with greater accuracy, providing more comprehensive health insights.
- Personalized Medication Management Systems: Wearable devices that automatically dispense medication at prescribed times, track adherence, and alert caregivers or healthcare providers to missed doses.
- Enhanced Fall Detection and Prevention: Wearables equipped with sophisticated sensors and AI algorithms to detect falls more accurately, and even predict the likelihood of falls based on gait analysis and other factors.
- Seamless Integration with Telehealth Platforms: Wearable devices that seamlessly integrate with telehealth platforms, enabling remote monitoring, virtual consultations, and remote patient management by healthcare providers.
Illustrative Examples of Wearable Health Tech for Seniors
Wearable health technology offers significant potential for improving the lives of senior citizens by providing convenient and accessible health monitoring and support. The following examples showcase the positive impact these devices can have on the health and well-being of older adults.
Several studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of wearable technology in improving various aspects of senior health. These improvements range from increased physical activity and better medication adherence to earlier detection of health issues and reduced hospital readmissions. The following examples highlight specific devices and their impact.
A Case Study: Improved Fall Prevention with a Smartwatch
Mrs. Eleanor Vance, a 78-year-old living independently, experienced several near-falls in her home. Concerned about her safety, her family purchased her a smartwatch equipped with fall detection capabilities. This particular smartwatch, the. “Guardian Angel,” uses a combination of accelerometers and gyroscopes to detect sudden changes in. Movement indicative of a fall. If a fall is detected, the watch automatically sends an alert to pre-programmed emergency contacts, including her daughter and her physician.
The watch also incorporates . GPS tracking, allowing emergency services to locate her quickly in case of a fall outside the home. Since using the Guardian Angel, Mrs. Vance has experienced a significant reduction in her anxiety about falling, leading to increased mobility and participation in her daily activities. The rapid response system provided by the watch has also given her family considerable peace of mind.
The device’s ease of use and comfortable design contributed significantly to its successful integration into her daily routine.
Design and Functionality of a Medication Adherence Device
This device, called the “Medi-minder,” is designed as a sleek, wrist-worn bracelet. Its casing is made of hypoallergenic, lightweight silicone in a variety of colours to appeal to diverse preferences. The face of the device features a clear, easy-to-read LCD screen displaying the time and medication reminders. The bracelet incorporates a small, internal compartment for holding a single daily dose of medication in pre-sorted blister packs.
At pre-programmed times, the device vibrates gently to remind the user to take their medication. If the medication is not taken within a specified timeframe, the device sends an alert to a designated caregiver or family member via a linked smartphone app. The app also allows caregivers to monitor medication adherence remotely and track medication consumption patterns.
The Medi-minder’s design prioritizes simplicity and ease of use, avoiding complex interfaces or confusing features. The battery life is designed for at least 7 days to minimize the frequency of charging.
Wearable health technology presents a powerful tool for enhancing the lives of seniors, promoting healthier aging, and supporting independent living. While challenges remain regarding cost, accessibility, and data privacy. Ongoing innovation and a focus on user-friendly design are paving the way for widespread adoption.
FAQ Corner
What are the privacy concerns surrounding wearable health tech for seniors?
Concerns exist regarding the security and privacy of personal health data collected by wearable devices. Data breaches and unauthorized access are potential risks, and clear guidelines on data usage and storage are crucial.
How can I choose the right wearable device for a senior loved one?
Consider their specific health needs, technological proficiency, and physical abilities. Ease of use, battery life, and the availability of support are also important factors. Consulting with their physician is recommended.
Are wearable health devices covered by insurance?
Coverage varies depending on the device, insurance plan, and the individual’s health needs. Some insurance providers may cover certain devices, particularly those prescribed by a physician for managing chronic conditions. It’s essential to check with your insurance provider.
What if a senior is hesitant to use wearable technology?
Introduce the device gradually, focusing on its benefits and addressing any concerns. Provide ample training and support, and consider starting with a simpler device before progressing to more complex ones. Patience and encouragement are key.
How accurate are the health readings from wearable devices?
Accuracy varies depending on the device and the specific metric being measured.
